|
Geant4
9.6.p02
|
|
Geant4
9.6.p02
|
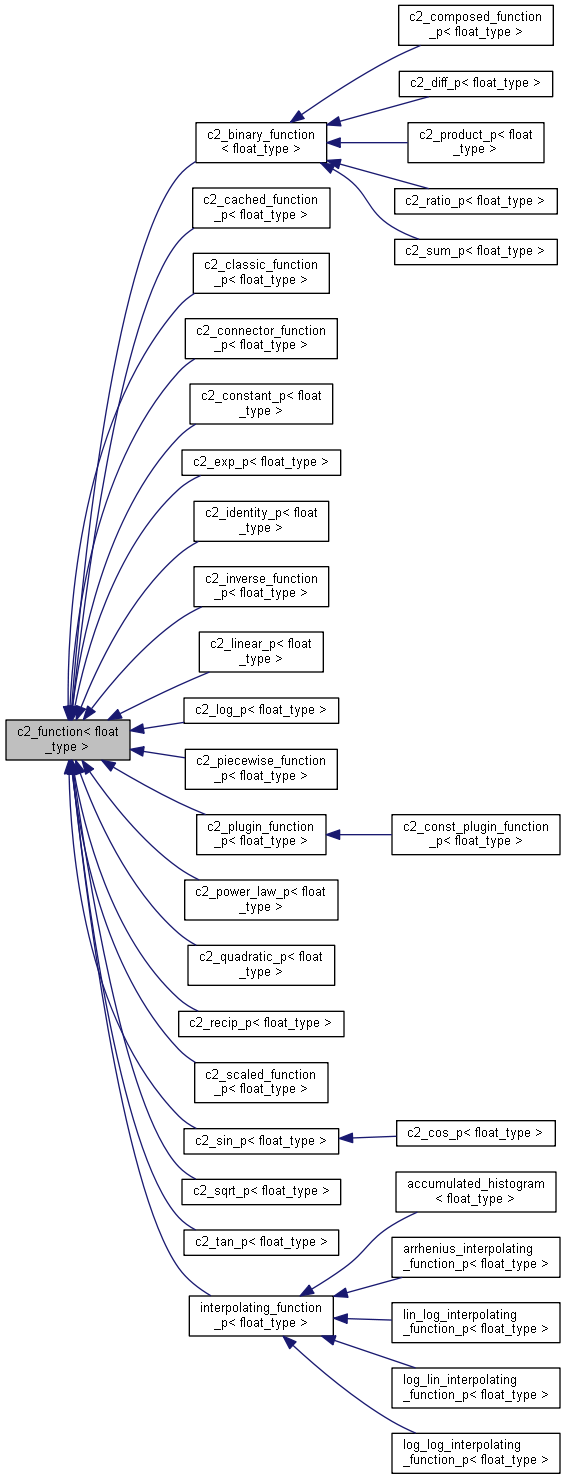
the parent class for all c2_functions.c2_functions know their value, first, and second derivative at almost every point. They can be efficiently combined with binary operators, via c2_binary_function, composed via c2_composed_function_, have their roots found via find_root(), and be adaptively integrated via partial_integrals() or integral(). They also can carry information with them about how to find 'interesting' points on the function. This information is set with set_sampling_grid() and extracted with get_sampling_grid(). More...
#include <c2_function.hh>
Public Member Functions | |
| const std::string | cvs_header_vers () const |
| get versioning information for the header file More... | |
| const std::string | cvs_file_vers () const |
| get versioning information for the source file More... | |
| virtual | ~c2_function () |
| destructor More... | |
| virtual float_type | value_with_derivatives (float_type x, float_type *yprime, float_type *yprime2) const =0 throw (c2_exception) |
| get the value and derivatives. More... | |
| float_type | operator() (float_type x) const throw (c2_exception) |
| evaluate the function in the classic way, ignoring derivatives. More... | |
| float_type | operator() (float_type x, float_type *yprime, float_type *yprime2) const throw (c2_exception) |
| get the value and derivatives. More... | |
| float_type | find_root (float_type lower_bracket, float_type upper_bracket, float_type start, float_type value, int *error=0, float_type *final_yprime=0, float_type *final_yprime2=0) const throw (c2_exception) |
| solve f(x)==value very efficiently, with explicit knowledge of derivatives of the function More... | |
| float_type | partial_integrals (std::vector< float_type > xgrid, std::vector< float_type > *partials=0, float_type abs_tol=1e-12, float_type rel_tol=1e-12, int derivs=2, bool adapt=true, bool extrapolate=true) const throw (c2_exception) |
| for points in xgrid, adaptively return Integral[f(x),{x,xgrid[i],xgrid[i+1]}] and return in vector, along with sum More... | |
| float_type | integral (float_type amin, float_type amax, std::vector< float_type > *partials=0, float_type abs_tol=1e-12, float_type rel_tol=1e-12, int derivs=2, bool adapt=true, bool extrapolate=true) const throw (c2_exception) |
| a fully-automated integrator which uses the information provided by the get_sampling_grid() function to figure out what to do. More... | |
| c2_piecewise_function_p < float_type > * | adaptively_sample (float_type amin, float_type amax, float_type abs_tol=1e-12, float_type rel_tol=1e-12, int derivs=2, std::vector< float_type > *xvals=0, std::vector< float_type > *yvals=0) const throw (c2_exception) |
| create a c2_piecewise_function_p from c2_connector_function_p segments which is a representation of the parent function to the specified accuracy, but maybe much cheaper to evaluate More... | |
| float_type | xmin () const |
| return the lower bound of the domain for this function as set by set_domain() More... | |
| float_type | xmax () const |
| return the upper bound of the domain for this function as set by set_domain() More... | |
| void | set_domain (float_type amin, float_type amax) |
| set the domain for this function. More... | |
| size_t | get_evaluations () const |
| this is a counter owned by the function but which can be used to monitor efficiency of algorithms. More... | |
| void | reset_evaluations () const |
| reset the counter More... | |
| void | increment_evaluations () const |
| count evaluations More... | |
| bool | check_monotonicity (const std::vector< float_type > &data, const char message[]) const throw (c2_exception) |
| check that a vector is monotonic, throw an exception if not, and return a flag if it is reversed More... | |
| virtual void | set_sampling_grid (const std::vector< float_type > &grid) throw (c2_exception) |
| establish a grid of 'interesting' points on the function. More... | |
| std::vector< float_type > * | get_sampling_grid_pointer () const |
| get the sampling grid, which may be a null pointer More... | |
| virtual void | get_sampling_grid (float_type amin, float_type amax, std::vector< float_type > &grid) const |
| return the grid of 'interesting' points along this function which lie in the region requested More... | |
| void | preen_sampling_grid (std::vector< float_type > *result) const |
| clean up endpoints on a grid of points More... | |
| void | refine_sampling_grid (std::vector< float_type > &grid, size_t refinement) const |
| refine a grid by splitting each interval into more intervals More... | |
| c2_function< float_type > & | normalized_function (float_type amin, float_type amax, float_type norm=1.0) const throw (c2_exception) |
| create a new c2_function from this one which is normalized on the interval More... | |
| c2_function< float_type > & | square_normalized_function (float_type amin, float_type amax, float_type norm=1.0) const throw (c2_exception) |
| create a new c2_function from this one which is square-normalized on the interval More... | |
| c2_function< float_type > & | square_normalized_function (float_type amin, float_type amax, const c2_function< float_type > &weight, float_type norm=1.0) const throw (c2_exception) |
| create a new c2_function from this one which is square-normalized with the provided weight on the interval More... | |
| c2_sum_p< float_type > & | operator+ (const c2_function< float_type > &rhs) const |
| factory function to create a c2_sum_p from a regular algebraic expression. More... | |
| c2_diff_p< float_type > & | operator- (const c2_function< float_type > &rhs) const |
| factory function to create a c2_diff_p from a regular algebraic expression. More... | |
| c2_product_p< float_type > & | operator* (const c2_function< float_type > &rhs) const |
| factory function to create a c2_product_p from a regular algebraic expression. More... | |
| c2_ratio_p< float_type > & | operator/ (const c2_function< float_type > &rhs) const |
| factory function to create a c2_ratio_p from a regular algebraic expression. More... | |
| c2_composed_function_p < float_type > & | operator() (const c2_function< float_type > &inner) const |
| compose this function outside another. More... | |
| float_type | get_trouble_point () const |
| Find out where a calculation ran into trouble, if it got a nan. If the most recent computation did not return a nan, this is undefined. More... | |
| void | claim_ownership () const |
| increment our reference count. Destruction is only legal if the count is zero. More... | |
| size_t | release_ownership_for_return () const throw (c2_exception) |
| decrement our reference count. Do not destroy at zero. More... | |
| void | release_ownership () const throw (c2_exception) |
| decrement our reference count. If the count reaches zero, destroy ourself. More... | |
| size_t | count_owners () const |
| get the reference count, mostly for debugging More... | |
| void | fill_fblock (c2_fblock< float_type > &fb) const throw (c2_exception) |
| fill in a c2_fblock<float_type>... a shortcut for the integrator & sampler More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| c2_function (const c2_function< float_type > &src) | |
| c2_function () | |
| virtual void | set_sampling_grid_pointer (std::vector< float_type > &grid) |
Protected Attributes | |
| std::vector< float_type > * | sampling_grid |
| bool | no_overwrite_grid |
| float_type | fXMin |
| float_type | fXMax |
| size_t | evaluations |
| float_type | bad_x_point |
| this point may be used to record where a calculation ran into trouble More... | |
the parent class for all c2_functions.
c2_functions know their value, first, and second derivative at almost every point. They can be efficiently combined with binary operators, via c2_binary_function, composed via c2_composed_function_, have their roots found via find_root(), and be adaptively integrated via partial_integrals() or integral(). They also can carry information with them about how to find 'interesting' points on the function. This information is set with set_sampling_grid() and extracted with get_sampling_grid().
Particularly important subclasses are the interpolating functions classes, interpolating_function , lin_log_interpolating_function, log_lin_interpolating_function, log_log_interpolating_function, and arrhenius_interpolating_function, as well as the template functions inverse_integrated_density_function().
For a discussion of memory management, see memory_management
Definition at line 138 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inlinevirtual |
destructor
Definition at line 152 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inlineprotected |
Definition at line 428 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inlineprotected |
Definition at line 432 of file c2_function.hh.
| c2_piecewise_function_p<float_type>* c2_function< float_type >::adaptively_sample | ( | float_type | amin, |
| float_type | amax, | ||
| float_type | abs_tol = 1e-12, |
||
| float_type | rel_tol = 1e-12, |
||
| int | derivs = 2, |
||
| std::vector< float_type > * | xvals = 0, |
||
| std::vector< float_type > * | yvals = 0 |
||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
create a c2_piecewise_function_p from c2_connector_function_p segments which is a representation of the parent function to the specified accuracy, but maybe much cheaper to evaluate
This method has three modes, depending on the derivs flag.
If derivs is 2, it computes a c2_piecewise_function_p representation of its parent function, which may be a much faster function to use in codes if the parent function is expensive. If xvals and yvals are non-null, it will also fill them in with the function values at each grid point the adaptive algorithm chooses.
If derivs is 1, this does not create the connectors, and returns an null pointer, but will fill in the xvals and yvals vectors with values of the function at points such that the linear interpolation error between the points is bounded by the tolerance values given. Because it uses derivative information from the function to manage the error control, it is almost completely free of issues with missing periods of oscillatory functions, even with no information provided in the sampling grid. This is typically useful for sampling a function for plotting.
If derivs is 0, this does something very like what it does if derivs = 1, but without derivatives. Instead, to compute the intermediate value of the function for error control, it just uses 3-point parabolic interpolation. This is useful amost exclusively for converting a non-c2_function, with no derivatives, but wrapped in a c2_classic_function wrapper, into a table of values to seed an interpolating_function_p. Note, however, that without derivatives, this is very susceptible to missing periods of oscillatory functions, so it is important to set a sampling grid which isn't too much coarser than the typical oscillations.
| amin | lower bound of the domain for sampling | |
| amax | upper bound of the domain for sampling | |
| abs_tol | the absolute error bound for each segment | |
| rel_tol | the fractional error bound for each segment. | |
| derivs | if 0 or 1, return a useless function, but fill in the xvals and yvals vectors (if non-null). Also, if 0 or 1, tolerances refer to linear interpolation, not high-order interpolation. If 2, return a full piecewise collection of c2_connector_function_p segments. See discussion above. | |
| [in,out] | xvals | vector of abscissas at which the function was actually sampled (if non-null) |
| [in,out] | yvals | vector of function values corresponding to xvals (if non-null) |
| bool c2_function< float_type >::check_monotonicity | ( | const std::vector< float_type > & | data, |
| const char | message[] | ||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
check that a vector is monotonic, throw an exception if not, and return a flag if it is reversed
| data | a vector of data points which are expected to be monotonic. |
| message | an informative string to include in an exception if this throws c2_exception |
|
inline |
increment our reference count. Destruction is only legal if the count is zero.
Definition at line 406 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
get the reference count, mostly for debugging
Definition at line 425 of file c2_function.hh.
| const std::string c2_function< float_type >::cvs_file_vers | ( | ) | const |
get versioning information for the source file
|
inline |
get versioning information for the header file
Definition at line 142 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline | ||||||||||||||
fill in a c2_fblock<float_type>... a shortcut for the integrator & sampler
| [in,out] | fb | the block to fill in with information |
Definition at line 456 of file c2_function.hh.
| float_type c2_function< float_type >::find_root | ( | float_type | lower_bracket, |
| float_type | upper_bracket, | ||
| float_type | start, | ||
| float_type | value, | ||
| int * | error = 0, |
||
| float_type * | final_yprime = 0, |
||
| float_type * | final_yprime2 = 0 |
||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
solve f(x)==value very efficiently, with explicit knowledge of derivatives of the function
find_root solves by iterated inverse quadratic extrapolation for a solution to f(x)=y. It includes checks against bad convergence, so it should never be able to fail. Unlike typical secant method or fancier Brent's method finders, this does not depend in any strong wasy on the brackets, unless the finder has to resort to successive approximations to close in on a root. Often, it is possible to make the brackets equal to the domain of the function, if there is any clue as to where the root lies, as given by the parameter start.
| lower_bracket | the lower bound for the search | |
| upper_bracket | the upper bound for the search. Function sign must be opposite to that at lower_bracket | |
| start | starting value for the search | |
| value | the value of the function being sought (solves f(x) = value) | |
| [out] | error | If pointer is zero, errors raise exception. Otherwise, returns error here. |
| [out] | final_yprime | If pointer is not zero, return derivative of function at root |
| [out] | final_yprime2 | If pointer is not zero, return second derivative of function at root |

|
inline |
this is a counter owned by the function but which can be used to monitor efficiency of algorithms.
It is not maintained automatically in general! The root finder, integrator, and sampler do increment it.
Definition at line 307 of file c2_function.hh.
|
virtual |
return the grid of 'interesting' points along this function which lie in the region requested
if a sampling grid is defined, work from there, otherwise return vector of (amin, amax)
| amin | the lower bound for which the function is to be sampled | |
| amax | the upper bound for which the function is to be sampled | |
| [in,out] | grid | filled vector containing the samplng grid. |
Reimplemented in c2_sin_p< float_type >, c2_plugin_function_p< float_type >, and c2_plugin_function_p< G4double >.
|
inline |
get the sampling grid, which may be a null pointer
Definition at line 332 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
Find out where a calculation ran into trouble, if it got a nan. If the most recent computation did not return a nan, this is undefined.
Definition at line 403 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
count evaluations
Definition at line 311 of file c2_function.hh.
| float_type c2_function< float_type >::integral | ( | float_type | amin, |
| float_type | amax, | ||
| std::vector< float_type > * | partials = 0, |
||
| float_type | abs_tol = 1e-12, |
||
| float_type | rel_tol = 1e-12, |
||
| int | derivs = 2, |
||
| bool | adapt = true, |
||
| bool | extrapolate = true |
||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
a fully-automated integrator which uses the information provided by the get_sampling_grid() function to figure out what to do.
It returns the integral of the function over the domain requested with error tolerances as specified. It is just a front-end to partial_integrals()
| amin | lower bound of the domain for integration |
| amax | upper bound of the domain for integration |
| partials | if non-NULL, a vector in which to receive the partial integrals. It will automatically be sized appropriately, if provided, to contain n - 1 elements where n is the length of xgrid |
| abs_tol | the absolute error bound for each segment |
| rel_tol | the fractional error bound for each segment. If the error is smaller than either the relative or absolute tolerance, the integration step is finished. |
| derivs | number of derivatives to trust, which sets the order of the integrator. The order is 3*derivs + 4. derivs can be 0, 1, or 2. |
| adapt | if true, use recursive adaptation, otherwise do simple evaluation on the grid provided with no error checking. |
| extrapolate | if true, use simple Richardson extrapolation on the final 2 steps to reduce the error. |
| c2_function<float_type>& c2_function< float_type >::normalized_function | ( | float_type | amin, |
| float_type | amax, | ||
| float_type | norm = 1.0 |
||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
create a new c2_function from this one which is normalized on the interval
| amin | lower bound of the domain for integration |
| amax | upper bound of the domain for integration |
| norm | the desired integral for the function over the region |
|
inline | ||||||||||||||
evaluate the function in the classic way, ignoring derivatives.
| x | the point at which to evaluate |
Definition at line 176 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
get the value and derivatives.
| [in] | x | the point at which to evaluate the function |
| [out] | yprime | the first derivative (if pointer is non-null) |
| [out] | yprime2 | the second derivative (if pointer is non-null) |
Definition at line 185 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
compose this function outside another.
| inner | the inner function |
Definition at line 397 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
factory function to create a c2_product_p from a regular algebraic expression.
| rhs | the right-hand term of the product |
Definition at line 386 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
factory function to create a c2_sum_p from a regular algebraic expression.
| rhs | the right-hand term of the sum |
Definition at line 376 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
factory function to create a c2_diff_p from a regular algebraic expression.
| rhs | the right-hand term of the difference |
Definition at line 381 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
factory function to create a c2_ratio_p from a regular algebraic expression.
| rhs | the right-hand term of the ratio (the denominator) |
Definition at line 391 of file c2_function.hh.
| float_type c2_function< float_type >::partial_integrals | ( | std::vector< float_type > | xgrid, |
| std::vector< float_type > * | partials = 0, |
||
| float_type | abs_tol = 1e-12, |
||
| float_type | rel_tol = 1e-12, |
||
| int | derivs = 2, |
||
| bool | adapt = true, |
||
| bool | extrapolate = true |
||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
for points in xgrid, adaptively return Integral[f(x),{x,xgrid[i],xgrid[i+1]}] and return in vector, along with sum
partial_integrals uses a method with an error O(dx**10) with full information from the derivatives, and falls back to lower order methods if informed of incomplete derivatives. It uses exact midpoint splitting of the intervals for recursion, resulting in no recomputation of the function during recursive descent at previously computed points.
| xgrid | points between which to evaluate definite integrals. |
| partials | if non-NULL, a vector in which to receive the partial integrals. It will automatically be sized apprpropriately, if provided, to contain n - 1 elements where n is the length of xgrid |
| abs_tol | the absolute error bound for each segment |
| rel_tol | the fractional error bound for each segment. If the error is smaller than either the relative or absolute tolerance, the integration step is finished. |
| derivs | number of derivatives to trust, which sets the order of the integrator. The order is 3*derivs + 4. derivs can be 0, 1, or 2. |
| adapt | if true, use recursive adaptation, otherwise do simple evaluation on the grid provided with no error checking. |
| extrapolate | if true, use simple Richardson extrapolation on the final 2 steps to reduce the error. |
| void c2_function< float_type >::preen_sampling_grid | ( | std::vector< float_type > * | result) | const |
clean up endpoints on a grid of points
| [in,out] | result | the sampling grid with excessively closely space endpoints removed. The grid is modified in place. |
| void c2_function< float_type >::refine_sampling_grid | ( | std::vector< float_type > & | grid, |
| size_t | refinement | ||
| ) | const |
refine a grid by splitting each interval into more intervals
| [in,out] | grid | the grid to refine in place |
| refinement | the number of new steps for each old step |
|
inline | |||||||||||||
decrement our reference count. If the count reaches zero, destroy ourself.
Definition at line 420 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline | |||||||||||||
decrement our reference count. Do not destroy at zero.
Definition at line 409 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
reset the counter
Definition at line 309 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
set the domain for this function.
Definition at line 301 of file c2_function.hh.
|
virtual | ||||||||||||||
establish a grid of 'interesting' points on the function.
The sampling grid describes a reasonable initial set of points to look at the function. this should generally be set at a scale which is quite coarse, and sufficient for initializing adaptive integration or possibly root bracketing. For sampling a function to build a new interpolating function, one may want to refine this for accuracy. However, interpolating_functions themselves return their original X grid by default, so refining the grid in this case might be a bad idea.
| grid | a vector of abscissas. The contents is copied into an internal vector, so the grid can be discarded after passingin. |
|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
| c2_function<float_type>& c2_function< float_type >::square_normalized_function | ( | float_type | amin, |
| float_type | amax, | ||
| float_type | norm = 1.0 |
||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
create a new c2_function from this one which is square-normalized on the interval
| amin | lower bound of the domain for integration |
| amax | upper bound of the domain for integration |
| norm | the desired integral for the function over the region |
| c2_function<float_type>& c2_function< float_type >::square_normalized_function | ( | float_type | amin, |
| float_type | amax, | ||
| const c2_function< float_type > & | weight, | ||
| float_type | norm = 1.0 |
||
| ) | const | ||
| throw | ( | c2_exception | |
| ) | |||
create a new c2_function from this one which is square-normalized with the provided weight on the interval
| amin | lower bound of the domain for integration |
| amax | upper bound of the domain for integration |
| weight | a c2_function providing the weight |
| norm | the desired integral for the function over the region |
|
pure virtual | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
get the value and derivatives.
There is required checking for null pointers on the derivatives, and most implementations should operate faster if derivatives are not needed.
| [in] | x | the point at which to evaluate the function |
| [out] | yprime | the first derivative (if pointer is non-null) |
| [out] | yprime2 | the second derivative (if pointer is non-null) |
Implemented in c2_piecewise_function_p< float_type >, c2_connector_function_p< float_type >, c2_inverse_function_p< float_type >, c2_power_law_p< float_type >, c2_quadratic_p< float_type >, c2_linear_p< float_type >, c2_linear_p< G4double >, c2_identity_p< float_type >, c2_recip_p< float_type >, c2_sqrt_p< float_type >, c2_exp_p< float_type >, c2_log_p< float_type >, c2_tan_p< float_type >, c2_cos_p< float_type >, c2_sin_p< float_type >, interpolating_function_p< float_type >, c2_constant_p< float_type >, c2_cached_function_p< float_type >, c2_scaled_function_p< float_type >, c2_binary_function< float_type >, c2_plugin_function_p< float_type >, c2_plugin_function_p< G4double >, and c2_classic_function_p< float_type >.
|
inline |
return the upper bound of the domain for this function as set by set_domain()
Definition at line 299 of file c2_function.hh.
|
inline |
return the lower bound of the domain for this function as set by set_domain()
Definition at line 297 of file c2_function.hh.
|
mutableprotected |
this point may be used to record where a calculation ran into trouble
Definition at line 452 of file c2_function.hh.
|
mutableprotected |
Definition at line 450 of file c2_function.hh.
|
protected |
Definition at line 449 of file c2_function.hh.
|
protected |
Definition at line 449 of file c2_function.hh.
|
protected |
Definition at line 447 of file c2_function.hh.
|
protected |
Definition at line 446 of file c2_function.hh.
 1.8.4
1.8.4