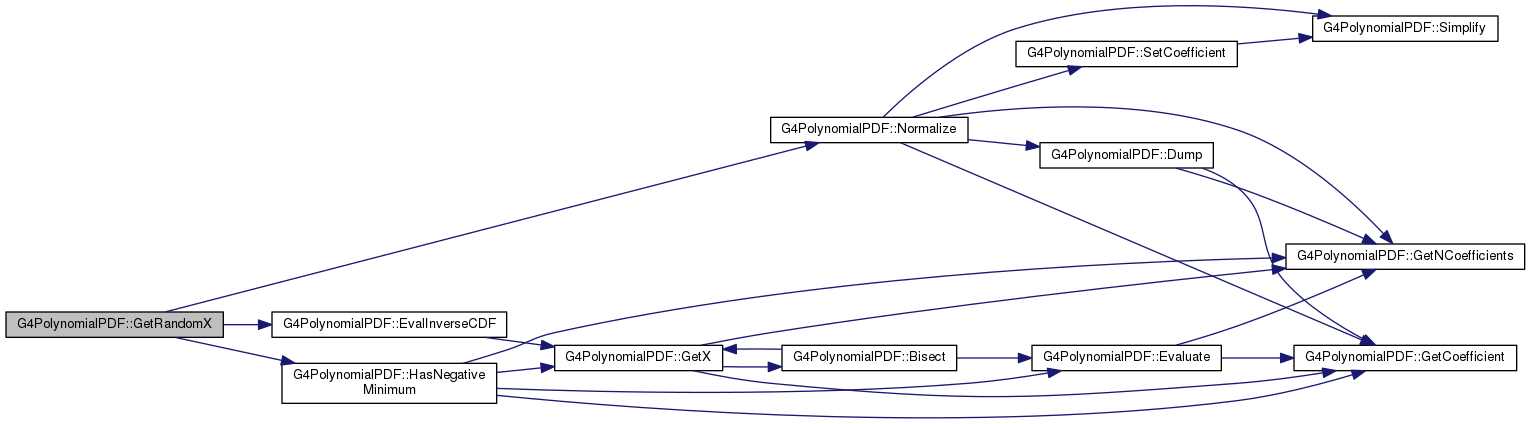
#include <G4PolynomialPDF.hh>
|
| | G4PolynomialPDF (size_t n=0, const double *coeffs=nullptr, G4double x1=0, G4double x2=1) |
| |
| | ~G4PolynomialPDF () |
| |
| void | SetNCoefficients (size_t n) |
| |
| size_t | GetNCoefficients () const |
| |
| void | SetCoefficients (const std::vector< G4double > &v) |
| |
| G4double | GetCoefficient (size_t i) const |
| |
| void | SetCoefficient (size_t i, G4double value, bool doSimplify) |
| |
| void | SetCoefficients (size_t n, const G4double *coeffs) |
| |
| void | Simplify () |
| |
| void | SetDomain (G4double x1, G4double x2) |
| |
| void | Normalize () |
| |
| G4double | Evaluate (G4double x, G4int ddxPower=0) |
| |
| G4double | GetRandomX () |
| |
| void | SetTolerance (G4double tolerance) |
| |
| G4double | GetX (G4double p, G4double x1, G4double x2, G4int ddxPower=0, G4double guess=1.e99, G4bool bisect=true) |
| |
| G4double | EvalInverseCDF (G4double p) |
| |
| G4double | Bisect (G4double p, G4double x1, G4double x2) |
| |
| void | Dump () |
| |
Definition at line 49 of file G4PolynomialPDF.hh.
| G4PolynomialPDF::G4PolynomialPDF |
( |
size_t |
n = 0, |
|
|
const double * |
coeffs = nullptr, |
|
|
G4double |
x1 = 0, |
|
|
G4double |
x2 = 1 |
|
) |
| |
Definition at line 43 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
void SetCoefficients(const std::vector< G4double > &v)
void SetNCoefficients(size_t n)
| G4PolynomialPDF::~G4PolynomialPDF |
( |
| ) |
|
Definition at line 392 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
397 if(fz < 0)
return Bisect(
p, z, x2);
G4double GetX(G4double p, G4double x1, G4double x2, G4int ddxPower=0, G4double guess=1.e99, G4bool bisect=true)
G4double Bisect(G4double p, G4double x1, G4double x2)
G4double Evaluate(G4double x, G4int ddxPower=0)
| void G4PolynomialPDF::Dump |
( |
| ) |
|
Definition at line 401 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
403 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::Dump() - PDF(x) = ";
408 if(i>1)
G4cout <<
"^" << i;
411 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::Dump() - Interval: " <<
fX1 <<
" <= x < "
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
G4double GetCoefficient(size_t i) const
size_t GetNCoefficients() const
Definition at line 102 of file G4PolynomialPDF.hh.
G4double GetX(G4double p, G4double x1, G4double x2, G4int ddxPower=0, G4double guess=1.e99, G4bool bisect=true)
Evaluate f(x) ddxPower = -1: f = CDF ddxPower = 0: f = PDF ddxPower = 1: f = (d/dx) PDF ddxPower = 2: f = (d2/dx2) PDF
Definition at line 131 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
138 if(ddxPower < -1 || ddxPower > 2) {
140 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: ddxPower " << ddxPower
141 <<
" not implemented" <<
G4endl;
155 else if(ddxPower == 1) {
158 else if(ddxPower == 2) {
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
G4double GetCoefficient(size_t i) const
size_t GetNCoefficients() const
| G4double G4PolynomialPDF::GetCoefficient |
( |
size_t |
i | ) |
const |
|
inline |
| size_t G4PolynomialPDF::GetNCoefficients |
( |
| ) |
const |
|
inline |
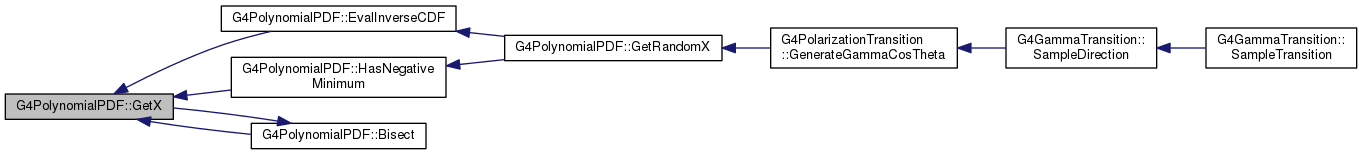
| G4double G4PolynomialPDF::GetRandomX |
( |
| ) |
|
Definition at line 207 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
213 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetRandomX() WARNING: PDF has negative values, returning 0..."
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
G4bool HasNegativeMinimum(G4double x1, G4double x2)
G4double EvalInverseCDF(G4double p)
Find a value of X between x1 and x2 at which f(x) = p. ddxPower = -1: f = CDF ddxPower = 0: f = PDF ddxPower = 1: f = (d/dx) PDF Uses the Newton-Raphson method to find the zero of f(x) - p. If not found in range, returns the nearest boundary
Definition at line 223 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
236 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: no PDF defined!" <<
G4endl;
240 if(ddxPower < -1 || ddxPower > 1) {
242 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: ddxPower " << ddxPower
243 <<
" not implemented" <<
G4endl;
249 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: p is out of range" <<
G4endl;
255 if(x2 <= x1 || x1 < fX1 || x2 >
fX2) {
257 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: domain must have fX1 <= x1 < x2 <= fX2. "
258 <<
"You sent x1 = " << x1 <<
", x2 = " << x2 <<
"." <<
G4endl;
275 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: Got slope = 0. "
276 <<
"Did you forget to Simplify()?" <<
G4endl;
280 if(ddxPower == 1) slope *= 2.;
285 else if(value > x2) {
300 if(ddxPower == 1) b *= 2.;
304 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: Got a = 0. "
305 <<
"Did you forget to Simplify()?" <<
G4endl;
309 if(ddxPower == 1) a *= 3;
310 else if(ddxPower == -1) a *= 0.5;
311 double sqrtFactor = b*b - 4.*a*
c;
312 if(sqrtFactor < 0)
return x2;
313 sqrtFactor = sqrt(sqrtFactor)/2./fabs(a);
314 G4double valueMinus = -b/2./a - sqrtFactor;
315 if(valueMinus >= x1 && valueMinus <= x2)
return valueMinus;
316 else if(valueMinus > x2)
return x2;
317 G4double valuePlus = -b/2./a + sqrtFactor;
318 if(valuePlus >= x1 && valuePlus <= x2)
return valuePlus;
319 else if(valuePlus < x1)
return x2;
320 return (x1-valueMinus <= valuePlus-x2) ? x1 : x2;
325 if(guess < x1 || guess > x2) guess = (x2+x1)*0.5;
327 size_t iterations = 0;
340 else if(ddxPower == 0) {
350 if(f == 0)
return guess;
353 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: got f != 0 but slope = 0 for ddxPower = "
358 lastChange = - f/dfdx;
360 if(guess + lastChange < x1) {
361 lastChange = x1 - guess;
362 }
else if(guess + lastChange > x2) {
363 lastChange = x2 - guess;
367 lastChange /= (fX2-
fX1);
370 if(iterations > 50) {
373 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: got stuck searching for " <<
p
374 <<
" between " << x1 <<
" and " << x2 <<
" with ddxPower = "
376 <<
". Last guess was " << guess <<
"." <<
G4endl;
379 if(ddxPower==-1 && bisect) {
381 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::GetX() WARNING: Bisceting and trying again..."
std::vector< ExP01TrackerHit * > a
G4double Bisect(G4double p, G4double x1, G4double x2)
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
G4double GetCoefficient(size_t i) const
const XML_Char int const XML_Char * value
size_t GetNCoefficients() const
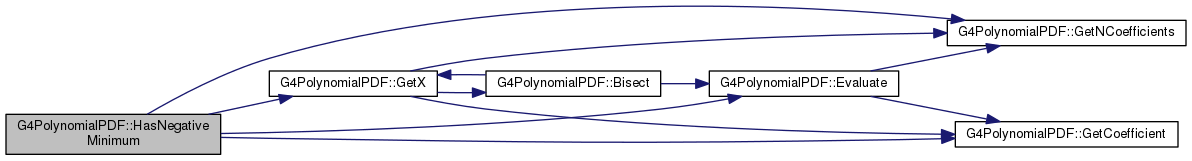
Definition at line 166 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
171 if(x1 < fX1 || x2 >
fX2 || x2 < x1) {
173 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::HasNegativeMinimum() WARNING: Invalid range "
174 << x1 <<
" - " << x2 <<
G4endl;
192 if(xMin < x1) xMin = x1;
193 if(xMin > x2) xMin = x2;
202 extremum >= x2-(x2-x1)*
fTolerance)
return false;
G4double GetX(G4double p, G4double x1, G4double x2, G4int ddxPower=0, G4double guess=1.e99, G4bool bisect=true)
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
G4double GetCoefficient(size_t i) const
G4bool HasNegativeMinimum(G4double x1, G4double x2)
size_t GetNCoefficients() const
G4double Evaluate(G4double x, G4int ddxPower=0)
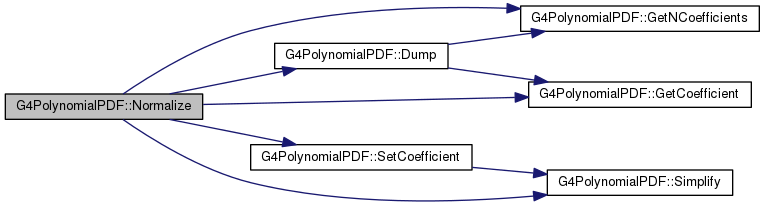
| void G4PolynomialPDF::Normalize |
( |
| ) |
|
Normalize PDF to 1 over domain fX1 to fX2. Double-check that the highest-order coefficient is non-zero.
Definition at line 100 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
118 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::Normalize() WARNING: PDF has non-positive area: "
std::vector< G4double > fCoefficients
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
G4double GetCoefficient(size_t i) const
size_t GetNCoefficients() const
void SetCoefficient(size_t i, G4double value, bool doSimplify)
| void G4PolynomialPDF::SetCoefficient |
( |
size_t |
i, |
|
|
G4double |
value, |
|
|
bool |
doSimplify |
|
) |
| |
Definition at line 54 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
std::vector< G4double > fCoefficients
const XML_Char int const XML_Char * value
| void G4PolynomialPDF::SetCoefficients |
( |
const std::vector< G4double > & |
v | ) |
|
|
inline |
| void G4PolynomialPDF::SetCoefficients |
( |
size_t |
n, |
|
|
const G4double * |
coeffs |
|
) |
| |
Definition at line 63 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
void SetNCoefficients(size_t n)
size_t GetNCoefficients() const
void SetCoefficient(size_t i, G4double value, bool doSimplify)
Definition at line 86 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
90 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::SetDomain() WARNING: Invalide domain! "
91 <<
"(x1 = " << x1 <<
", x2 = " << x2 <<
")." <<
G4endl;
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
| void G4PolynomialPDF::SetNCoefficients |
( |
size_t |
n | ) |
|
|
inline |
| void G4PolynomialPDF::Simplify |
( |
| ) |
|
Definition at line 74 of file G4PolynomialPDF.cc.
78 G4cout <<
"G4PolynomialPDF::Simplify() WARNING: had to pop coefficient "
std::vector< G4double > fCoefficients
G4GLOB_DLL std::ostream G4cout
| G4bool G4PolynomialPDF::fChanged |
|
protected |
| std::vector<G4double> G4PolynomialPDF::fCoefficients |
|
protected |
| G4int G4PolynomialPDF::fVerbose |
|
protected |
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: