|
Geant4
10.03.p03
|
|
Geant4
10.03.p03
|
#include <G4Nucleus.hh>
Definition at line 50 of file G4Nucleus.hh.
| G4Nucleus::G4Nucleus | ( | ) |
Definition at line 54 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
Definition at line 68 of file G4Nucleus.cc.

Definition at line 82 of file G4Nucleus.cc.

| G4Nucleus::G4Nucleus | ( | const G4Material * | aMaterial | ) |
Definition at line 96 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
| G4Nucleus::~G4Nucleus | ( | ) |
Definition at line 110 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
|
inline |
Definition at line 61 of file G4Nucleus.hh.
Definition at line 449 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
| void G4Nucleus::AddMomentum | ( | const G4ThreeVector | aMomentum | ) |
Definition at line 444 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
Definition at line 337 of file G4Nucleus.cc.


Definition at line 254 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
Definition at line 261 of file G4Nucleus.cc.

| void G4Nucleus::ChooseParameters | ( | const G4Material * | aMaterial | ) |
Definition at line 172 of file G4Nucleus.cc.

Definition at line 382 of file G4Nucleus.cc.

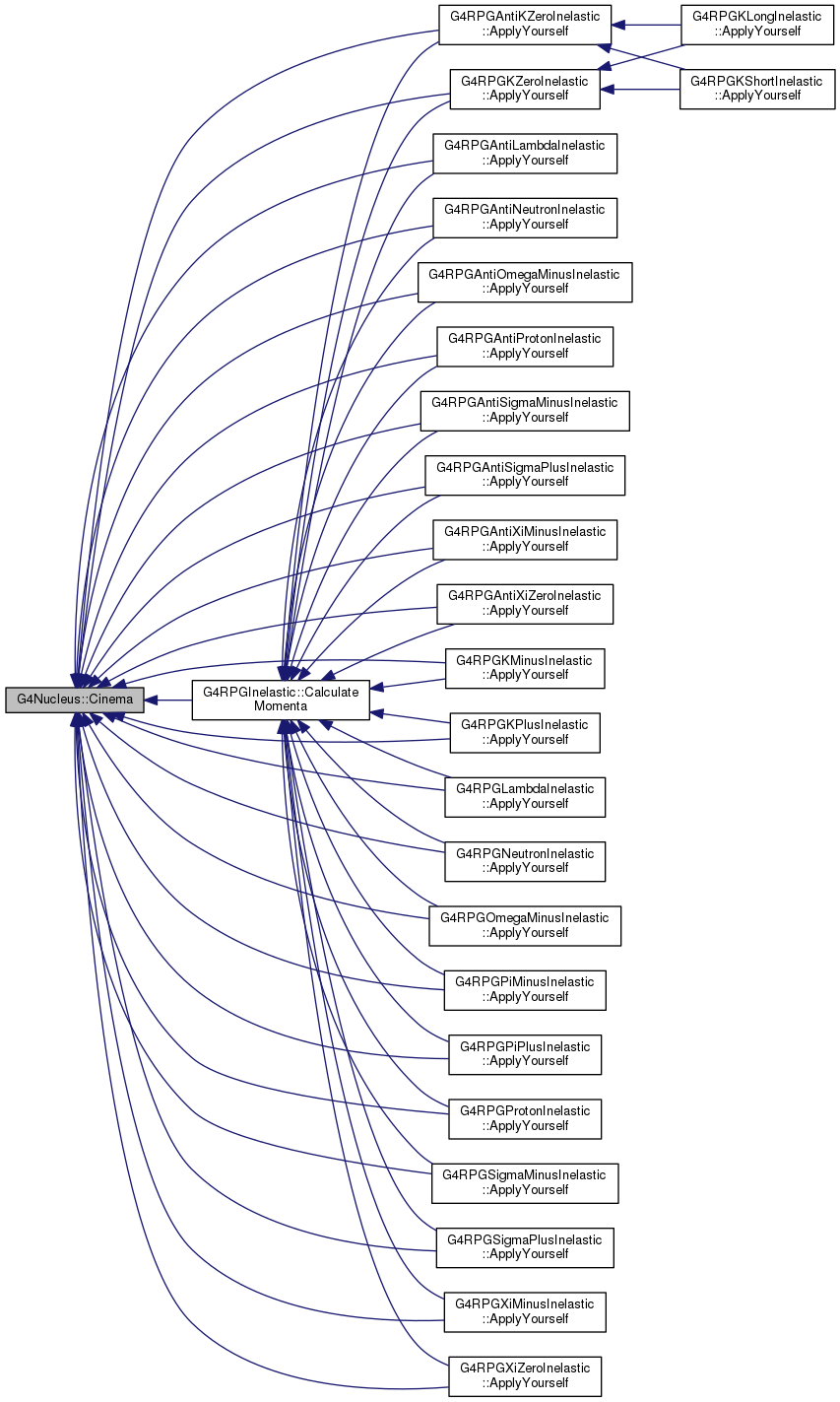
Definition at line 278 of file G4Nucleus.cc.


| G4ReactionProductVector * G4Nucleus::Fragmentate | ( | ) |
Definition at line 438 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
|
inline |
|
inline |
| G4ReactionProduct G4Nucleus::GetBiasedThermalNucleus | ( | G4double | aMass, |
| G4ThreeVector | aVelocity, | ||
| G4double | temp = -1 |
||
| ) | const |
Definition at line 113 of file G4Nucleus.cc.

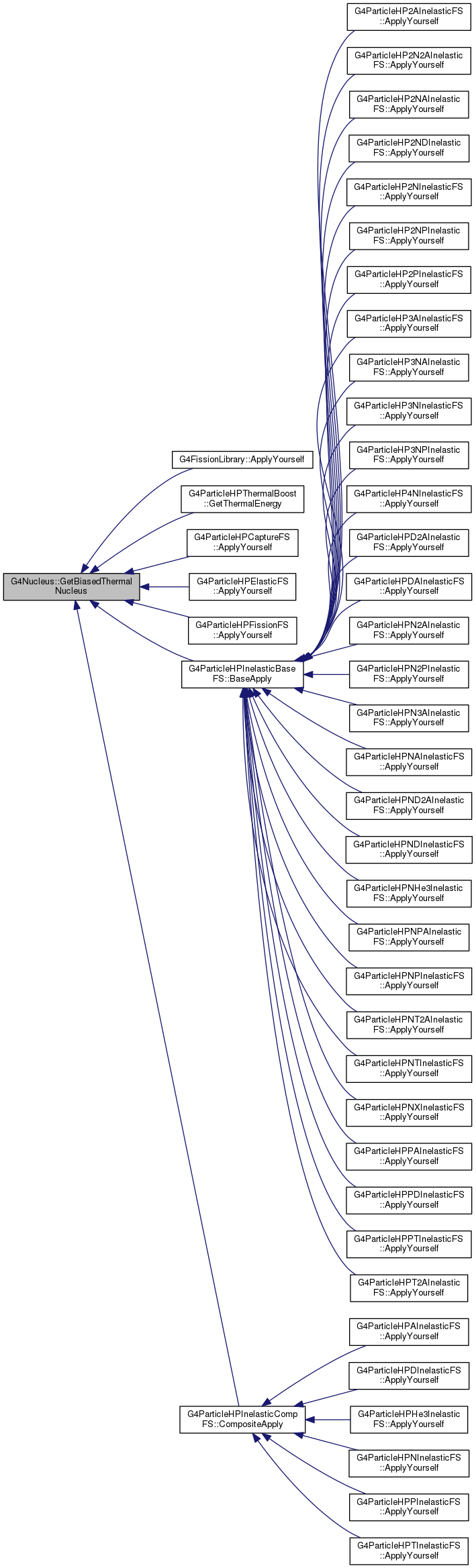
|
inline |
|
inline |
| G4ThreeVector G4Nucleus::GetFermiMomentum | ( | ) |
Definition at line 412 of file G4Nucleus.cc.


|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
| G4ReactionProduct G4Nucleus::GetThermalNucleus | ( | G4double | aMass, |
| G4double | temp = -1 |
||
| ) | const |
Definition at line 143 of file G4Nucleus.cc.


Definition at line 268 of file G4Nucleus.cc.

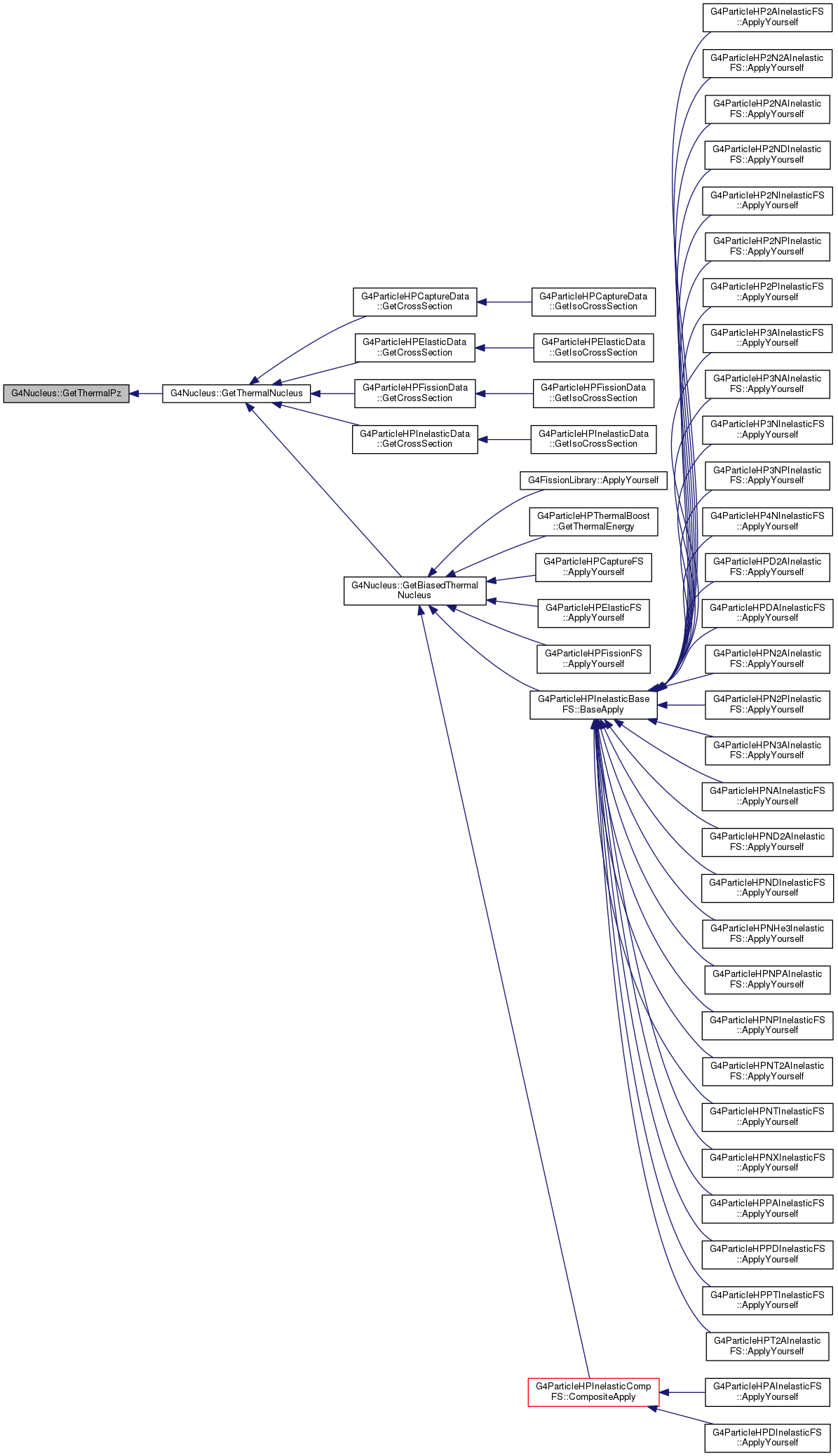
Definition at line 115 of file G4Nucleus.hh.
Definition at line 89 of file G4Nucleus.hh.
Definition at line 64 of file G4Nucleus.hh.
Definition at line 86 of file G4Nucleus.hh.
| G4DynamicParticle * G4Nucleus::ReturnTargetParticle | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 241 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
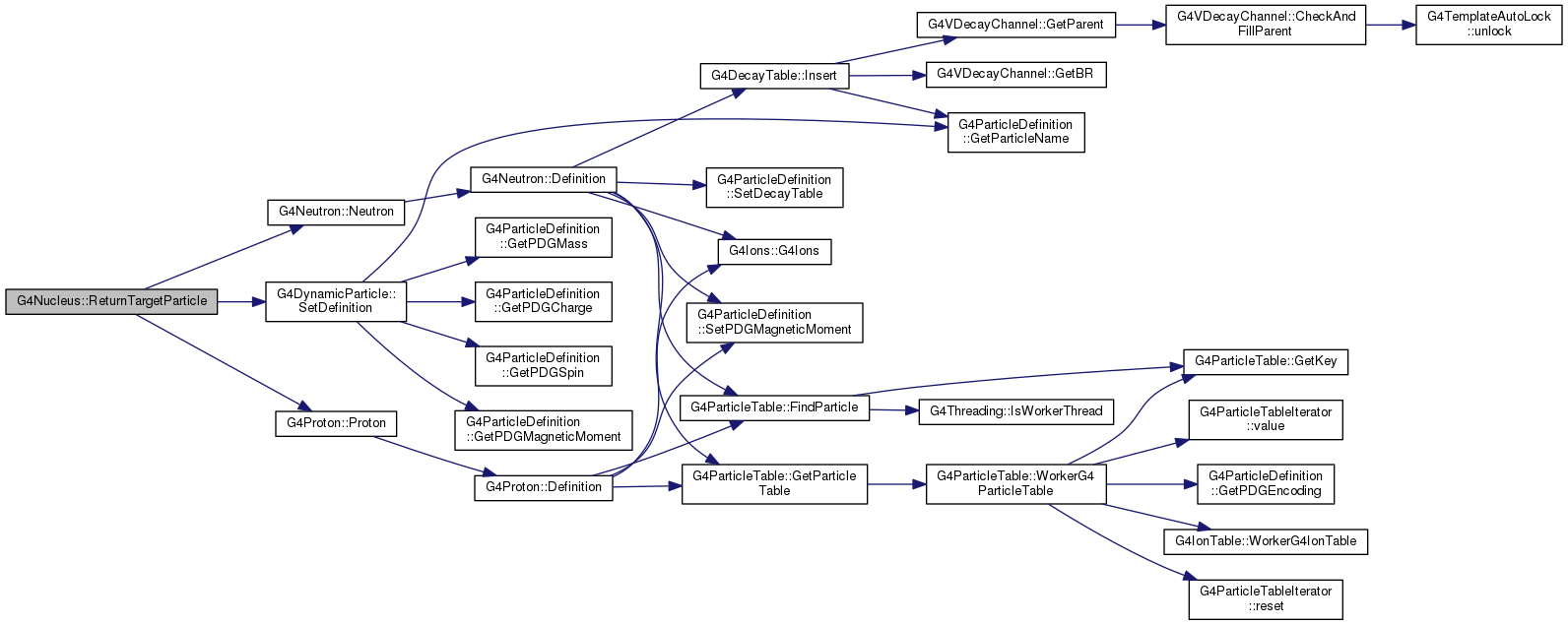

Definition at line 122 of file G4Nucleus.hh.

Definition at line 212 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
Definition at line 226 of file G4Nucleus.cc.
